These valves have an electromechanical mechanism to control them. The characteristics of the electric current used, the strength of the magnetic field produced, the mechanism used to control the fluid, and the fluid that is controlled vary between solenoid valves. The linear plunger-type, rocket, and pivoting armature actuators use distinct mechanisms. The valve uses a design with two ports for fluid regulation, or it can use a design with three or more ports to switch flows between ports. Valve placement on multiple manifold solenoids is contiguous. Read More…
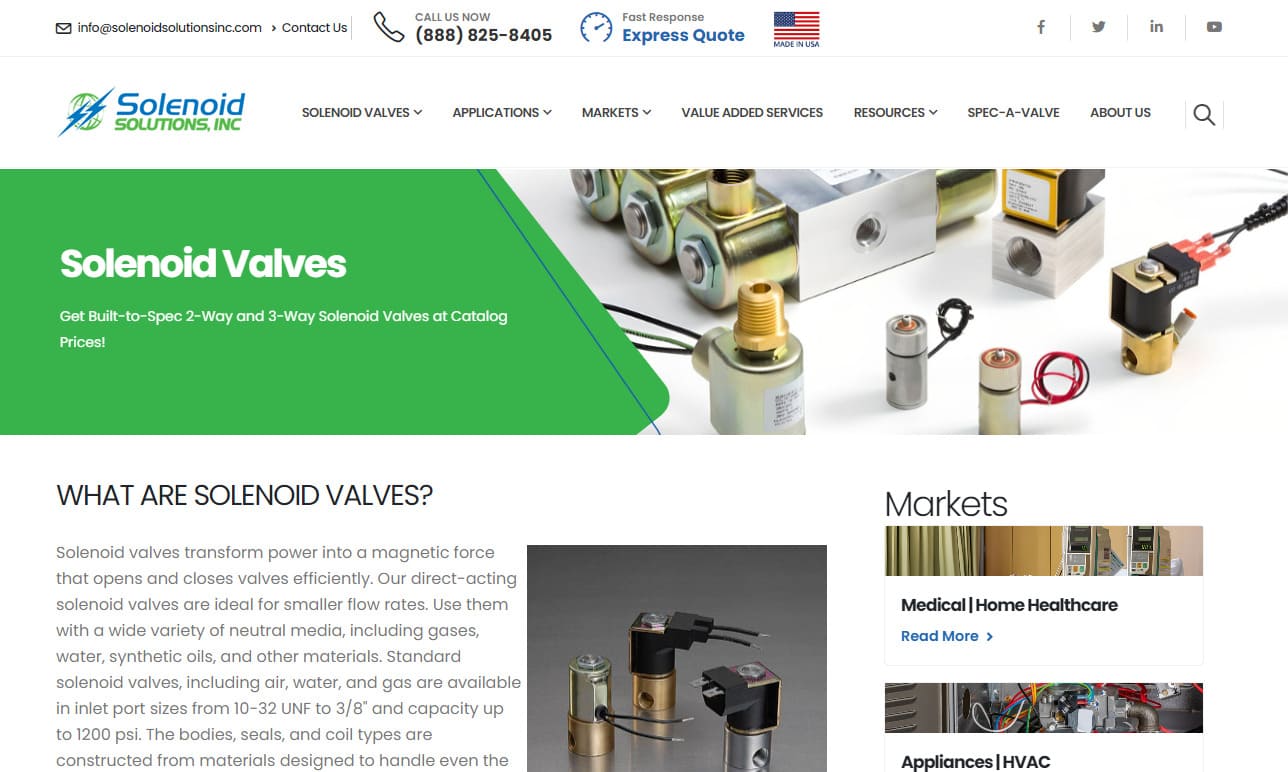
Solenoid Solutions manufacturers custom direct-acting 2 and 3-way solenoid valves and multi-valve manifolds for OEMs in the medical, appliance, transportation, power generation and industrial equipment markets.
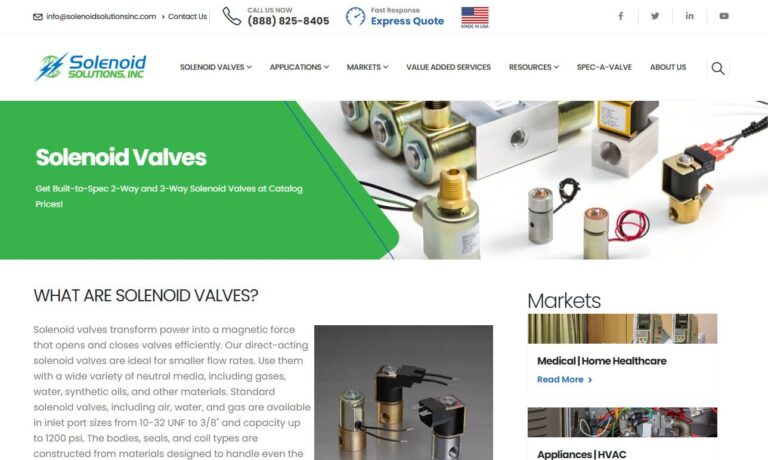
Our solenoid valves are all tested in house following very strict quality guidelines. We opened our doors in 1936 and ever since then we have been committed to bringing top of the line products and customer service that cannot be beat!
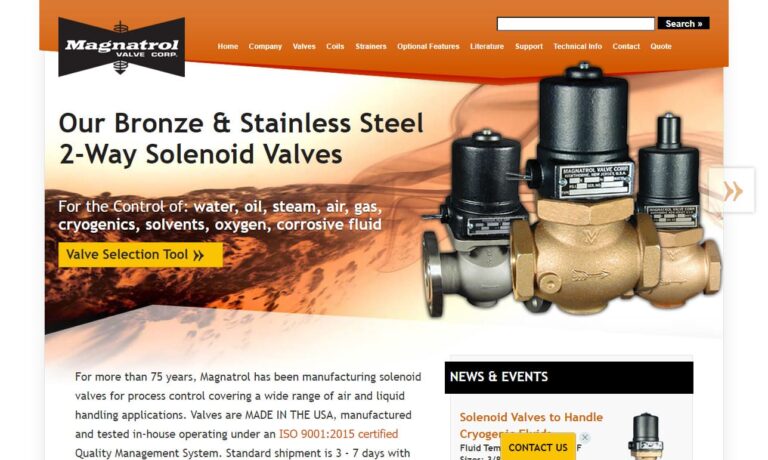
At Electric Solenoid Valves, we specialize in providing comprehensive solutions for solenoid valves, tailored to meet the diverse needs of our valued clientele. With expertise in fluid control systems, we have established ourselves as a trusted leader, known for our unwavering commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Our product offerings encompass a wide range of solenoid...
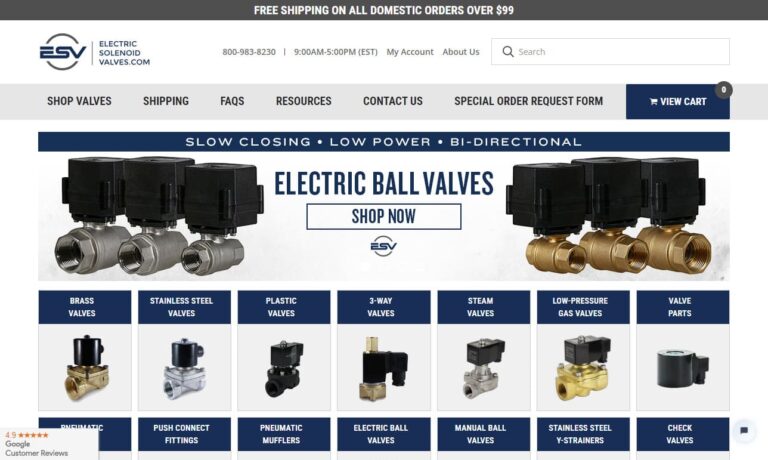
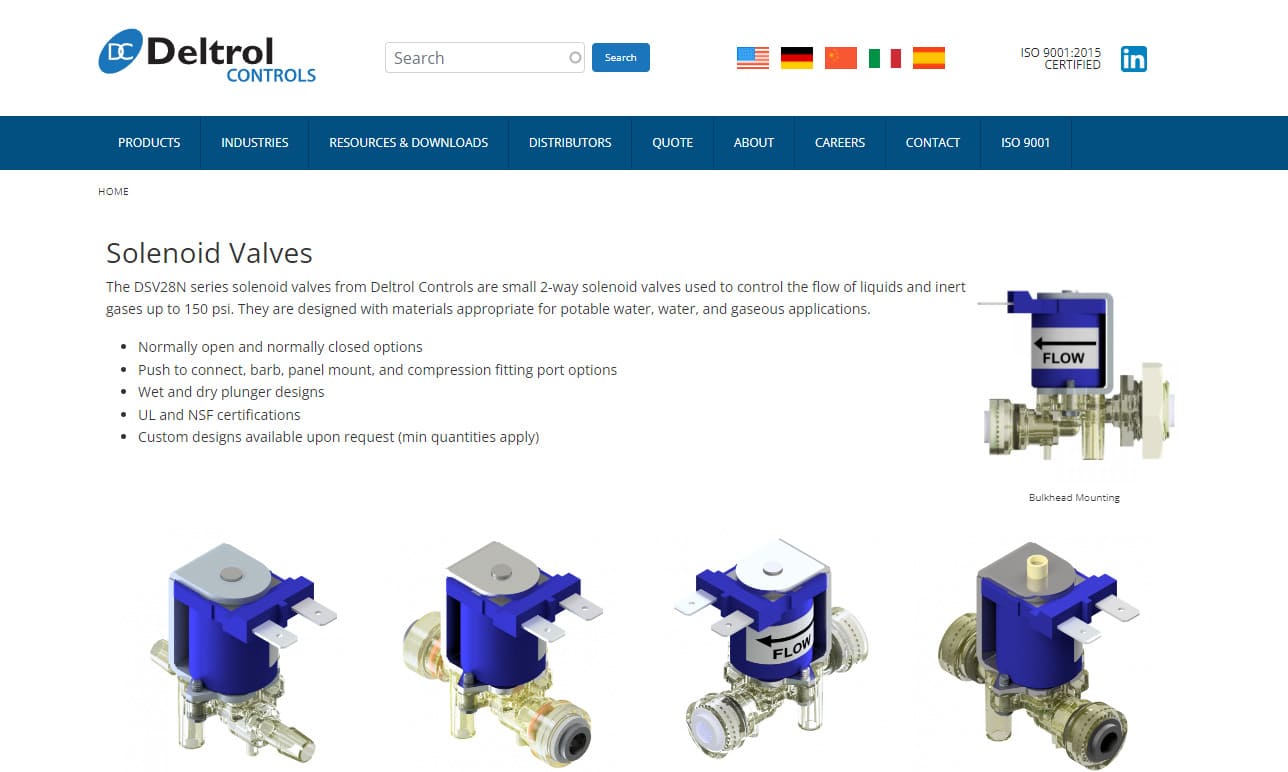
Deltrol Controls manufactures and designs a full line of stock and custom solenoids, electrical relays, dispensing valves, and custom switch assemblies. Customer satisfaction is our number one priority so we employ talented workers and stay up-to-date with the latest technology. Whatever your specific need is, Deltrol Controls has the solution. To receive a quote or more information please...
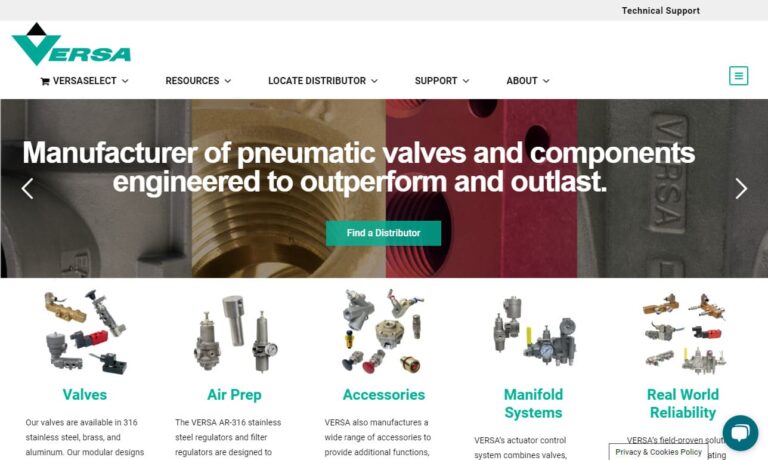
Versa® Products offers a wide range of pneumatic control valves, air valves and solenoid design. We have maintained our commitment to quality products and services since our company was established in 1949. We are a solenoid valve manufacturer, offering solenoids in brass and stainless steel.
More Electric Solenoid Valve Manufacturers

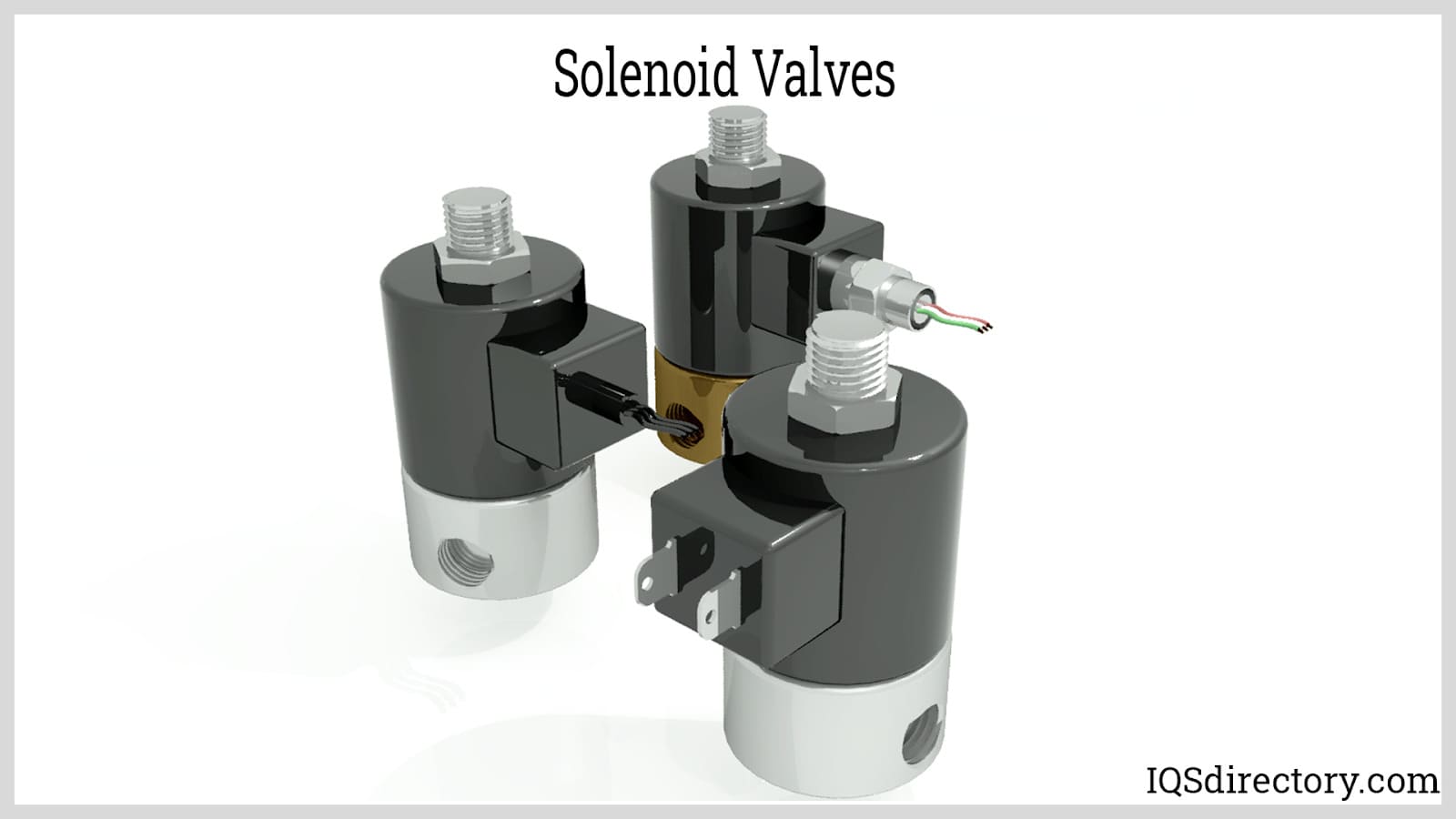
How Solenoid Valves Work
Different sorts of valve designs exist. The majority of valves contain numerous ports and fluid channels. The valve is said to be "usually open" when the solenoid is not activated, and it is open. The valve is said to be typically closed when the solenoid is not activated, and it is closed. Additionally, there are more intricate designs, such as three-way valves.
In a three-way valve, each of the three ports is connected to either the supply or exhaust ports. These valves can be classified according to how they function. For example, limited solenoids can only generate a small amount of force; if this force is adequate to close and open the valve, then direct-acting solenoids are practical.
Materials Applied in Solenoid Valves' Construction
The material chosen for the valve body should be fluid-compatible. The bodies of solenoid valves are mostly made of stainless steel, aluminum, brass, plastic, and brass. Additionally, the seals must work with fluid. The core, plug nut, shade ring, springs, and other components are also exposed to fluids, making them fluid-compatible to facilitate simpler sealing.
The core tube must be non-magnetic to allow the solenoid's field to pass through it and the plug nut. Iron or another material with strong magnetic characteristics is needed for the core and plug nut (but iron is more prone to corrosion). Because stainless steel is both magnetic and non-magnetic, it is frequently used.
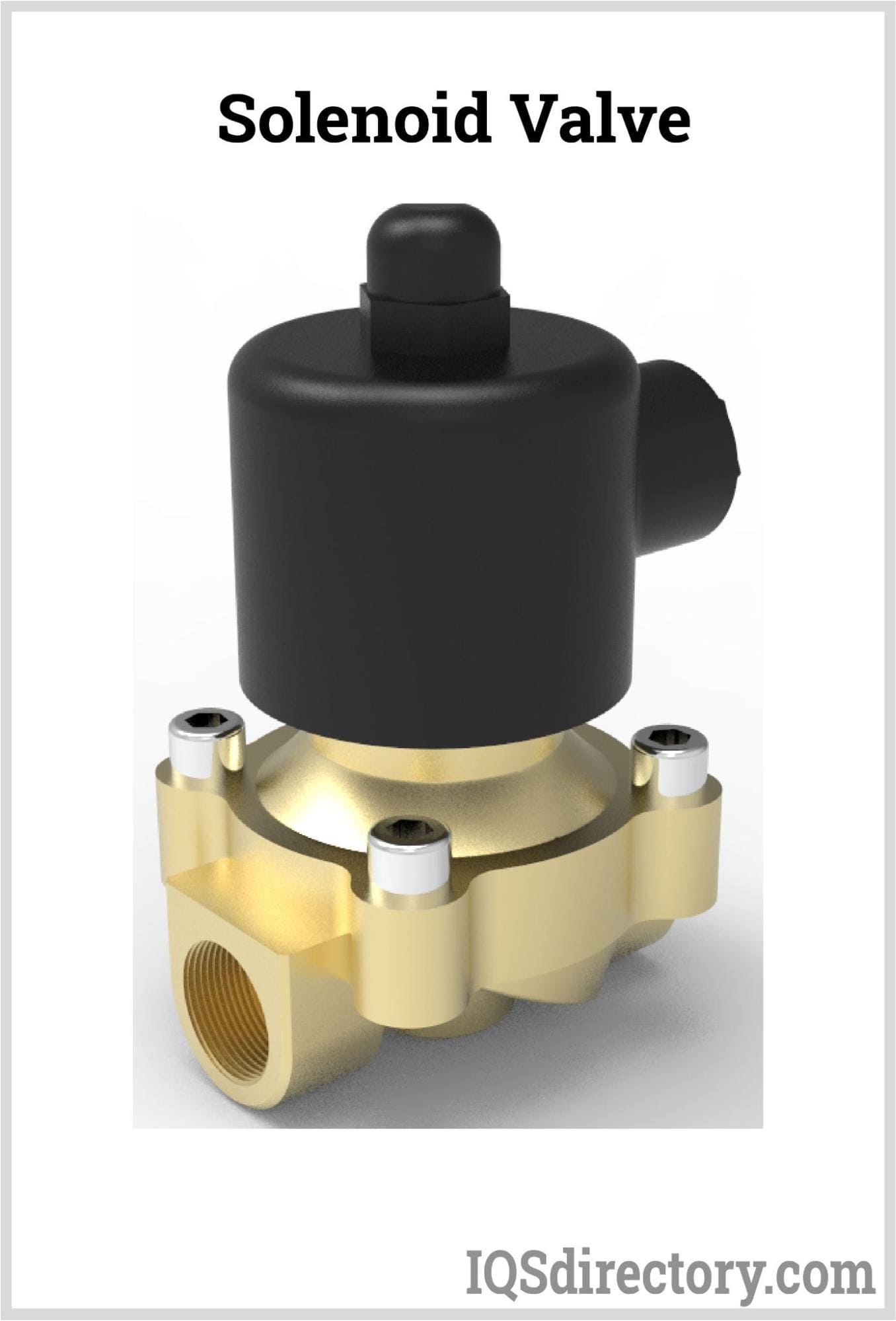
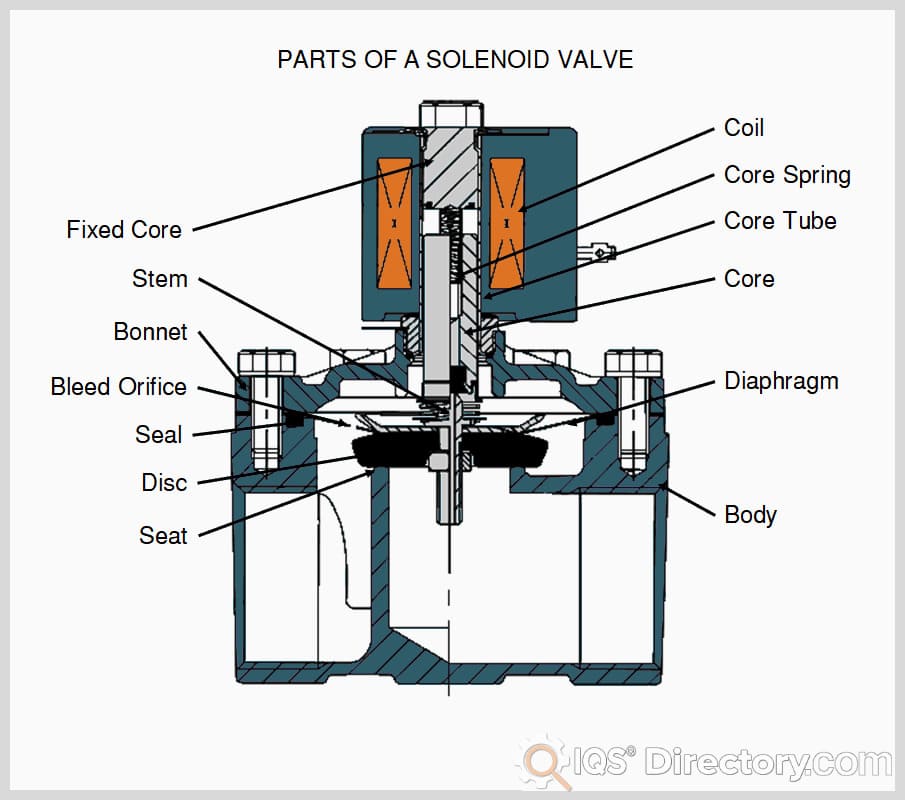
Solenoid Valve Components
The basic parts of a solenoid valve are as follows:
- Sub-assembly for a solenoid (core, core spring, shading coil, plug nut, core tube, solenoid coil, retaining clip)
- Core tube with a bonnet seal
- Diaphragm - body seal hanger spring diaphragm - bonnet
- Backup disk washer valve body
When the solenoid is powered up, the magnetic plunger or core of the valve moves, and the solenoid is coaxial with the plug nut and the core. The seals that govern the flow of fluid can be damaged or broken by the movement of the core. When the coil is not electrified, the spring will keep the core in its usual position. The fluid is sealed, and the core tube guides and holds the core while holding on to the plug nut.
The core tube must not be magnetic to maximize core mobility, as a magnetic core tube would provide a shunt path for field lines. In some designs, the core tube is an enclosed metal shell that simplifies the sealing problem because fluid cannot escape from the enclosure. Still, it also increases magnetic path resistance because the magnetic path must travel twice through the thickness of the core tube—once near the core and once near the plug nut.
Solenoid Valve Types
Direct Acting Valves (DAVs)
This kind of solenoid valve has a coil that, in direct action, magnetically opens the valve and raises both the shaft and the valve seat without relying on the outside pressure. Direct-acting solenoid valves can be opened at low power, but they must be powered fully during valve opening.

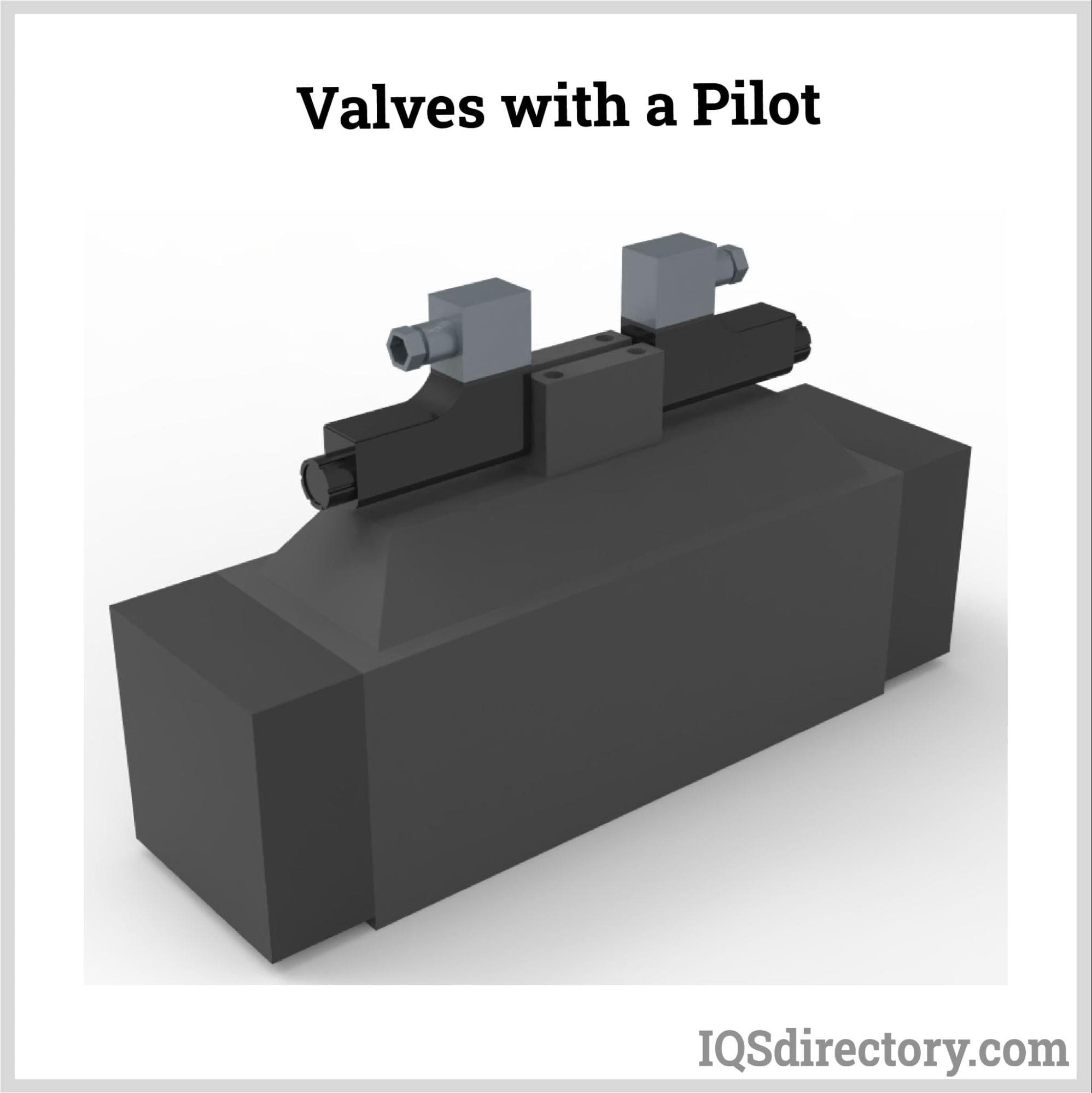
Valves With a Pilot
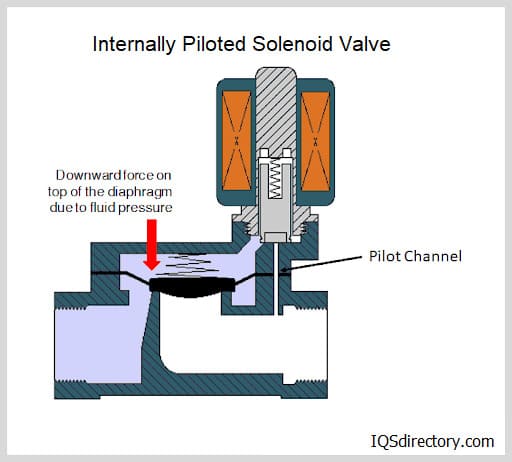
In pilot-operated valves, a smaller pilot valve is engaged by the solenoid, which then unlocks a larger valve that is working at very high pressure and is necessary for increased volume flow and releasing enormous quantities of gasses, steam, liquids, and air. As a result, piloted valves operate with a relatively low electrical energy requirement. Still, they can operate more slowly than direct-acting solenoid valves since they require full power to be maintained in the open position.
Three-Way Valves
Each of the two ports in a two-way valve is utilized one at a time to open and close the valve. The operation of a two-way valve can be set as generally closed or normally open. Until a current is applied to close the valve in the open state, it stays in that state. The valve automatically opens when the electricity is turned back on. Common solenoid valves that are typically closed operate in the opposite direction and stay closed until a power source opens them. Three-port three-way valves are used when exhaustive and alternative pressure is required for an operation, as in a coffee maker or dishwasher.
Four-Way Valves
The valves with four or more port connections are known as four-way valves. In most cases, they work using a dual-acting actuator or cylinder. In four-way valves, supply pressure is provided by the remaining port connections, while exhaust pressure is provided by half of the connections. These valves are universal, normally open, or normally closed.
Electric Solenoid Valves Applications
In automatic irrigation sprinklers with automatic controllers, electric solenoid valves are also utilized. Electric solenoid valves are also used in residential washing machines and dishwashers to control the amount of water that enters the appliance. Paintball gun triggers use these solenoid valves to operate the carbon dioxide hammer valve. Electric solenoid valves are utilized in various industrial applications, including general on-off control, pilot plant control loops, process control systems, calibration and test stands, and applications for manufacturing various pieces of equipment.
Solenoid Valve Benefits
- Reduced power use
- Repairs are affordable.
- Operated remotely
- Swiftness of reaction
- Able to work with both AC and DC voltage
- Use of both high and low temperatures
- Installed either vertically or horizontally



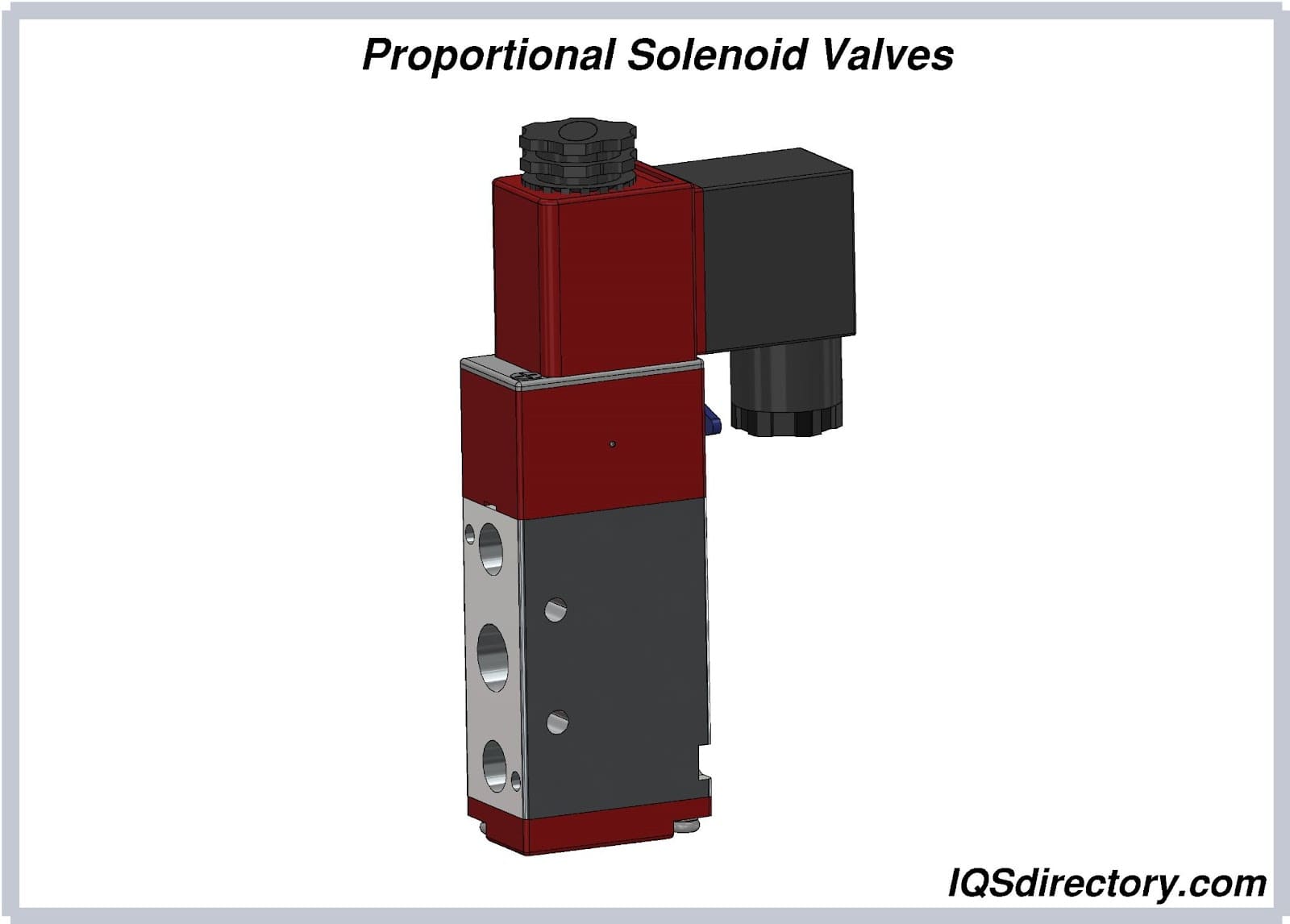

 Ball Valves
Ball Valves Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps Check Valves
Check Valves Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm Valves Flow Meters
Flow Meters Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic Valves Metering Pumps
Metering Pumps Solenoid Valves
Solenoid Valves Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services