A pneumatic valve is a device that alters or controls the movement of air (or another gas). They control the air or gas at the source and modify the rate it enters pipes, tubing, or other components as needed to function in an automated pneumatic system. There are often two different usage contexts for the phrase “pneumatic valve,” both of which are manufactured with industrial equipment. First, a pneumatic valve is a tool used to alter or control the movement of a gas in a pneumatic system. They control how much air or gas is introduced as needed into the pipes, tubing, or machinery of an automatic pneumatic system at the source. Read More…
Solenoid Solutions manufacturers custom direct-acting 2 and 3-way solenoid valves and multi-valve manifolds for OEMs in the medical, appliance, transportation, power generation and industrial equipment markets.
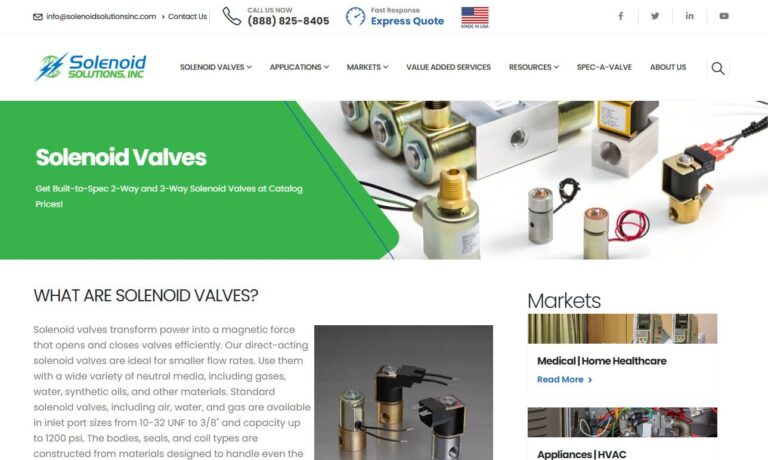
Our solenoid valves are all tested in house following very strict quality guidelines. We opened our doors in 1936 and ever since then we have been committed to bringing top of the line products and customer service that cannot be beat!
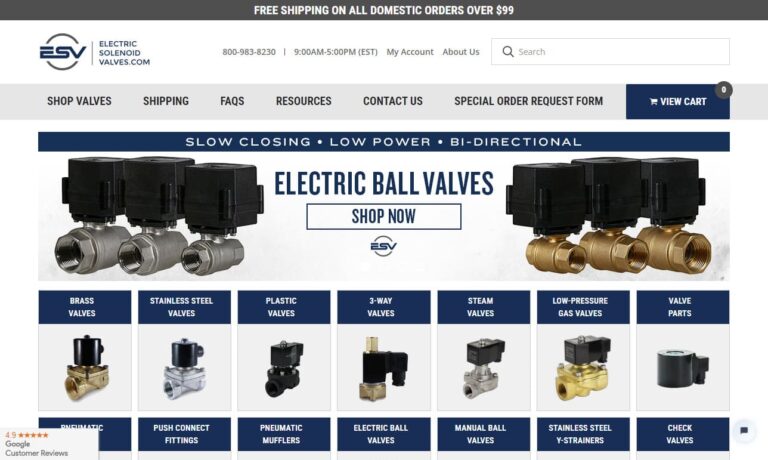
At Electric Solenoid Valves, we specialize in providing comprehensive solutions for solenoid valves, tailored to meet the diverse needs of our valued clientele. With expertise in fluid control systems, we have established ourselves as a trusted leader, known for our unwavering commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Our product offerings encompass a wide range of solenoid...
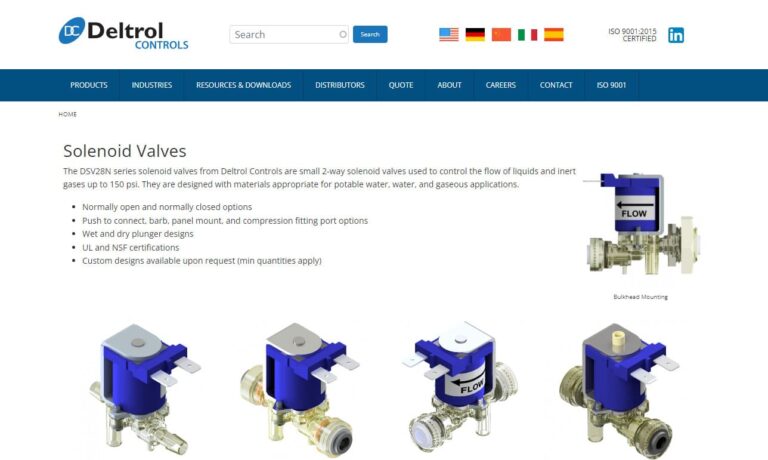
Deltrol Controls manufactures and designs a full line of stock and custom solenoids, electrical relays, dispensing valves, and custom switch assemblies. Customer satisfaction is our number one priority so we employ talented workers and stay up-to-date with the latest technology. Whatever your specific need is, Deltrol Controls has the solution. To receive a quote or more information please...
Versa® Products offers a wide range of pneumatic control valves, air valves and solenoid design. We have maintained our commitment to quality products and services since our company was established in 1949. We are a solenoid valve manufacturer, offering solenoids in brass and stainless steel.
More Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Manufacturers

The pneumatic valve can be opened or closed by several techniques, including manually, mechanically, pneumatically, and electrically via a solenoid or motorized actuator. It's crucial to remember that the pneumatic system controls and distributes pressurized air or gas through valve ports.
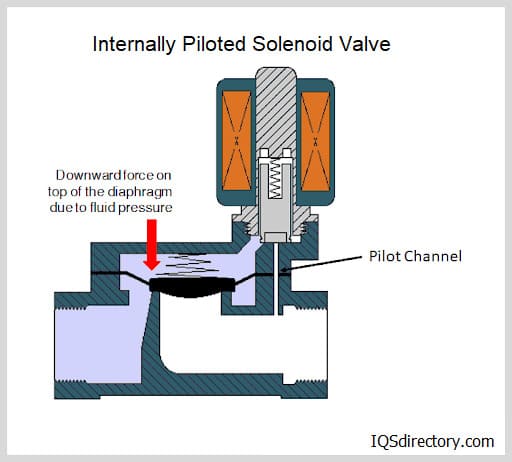
Alternately, in a pneumatic valve, a different fluid—possibly water or oil—flows through the ports of the valve in place of air. In this case, the fluid in the lines is not air; instead, the pneumatic actuator uses air as the control fluid to open, close, or modify the flow. These valves are hence referred to as pneumatically actuated valves.
Types of Pneumatic Valves
Pneumatic valves, also known as directional control valves, can be installed in different ways, including:
- Based on how many flow paths or switching possibilities they offer
- How many inlet and output ports they have
- How the ports open or close
- How the valve behaves when it is not in use
Pneumatic valves are categorized as functional directional control valves that can direct airflow or entirely halt it. These parts can be used in a hydraulic system in various ways, such as to connect or detach the system's main compressed air supply or to retract air cylinders that are a part of the process for which the pneumatic system was intended.
In light of this, the following categories can be used to generally classify pneumatic valves:
- Valves with two-way directional control
- Pneumatic three-way directional valves
- Four-way pneumatic valves with directional control
Spring Offset Pneumatic Valves
Directional control valves are essential components in every pneumatic circuit to manage the speed or order of operations. The flow routes under different operating conditions can be used to categorize directional-control valves. The number of ports, flow paths, and potential valve settings is significant determining factors. Here are a few basic setups.
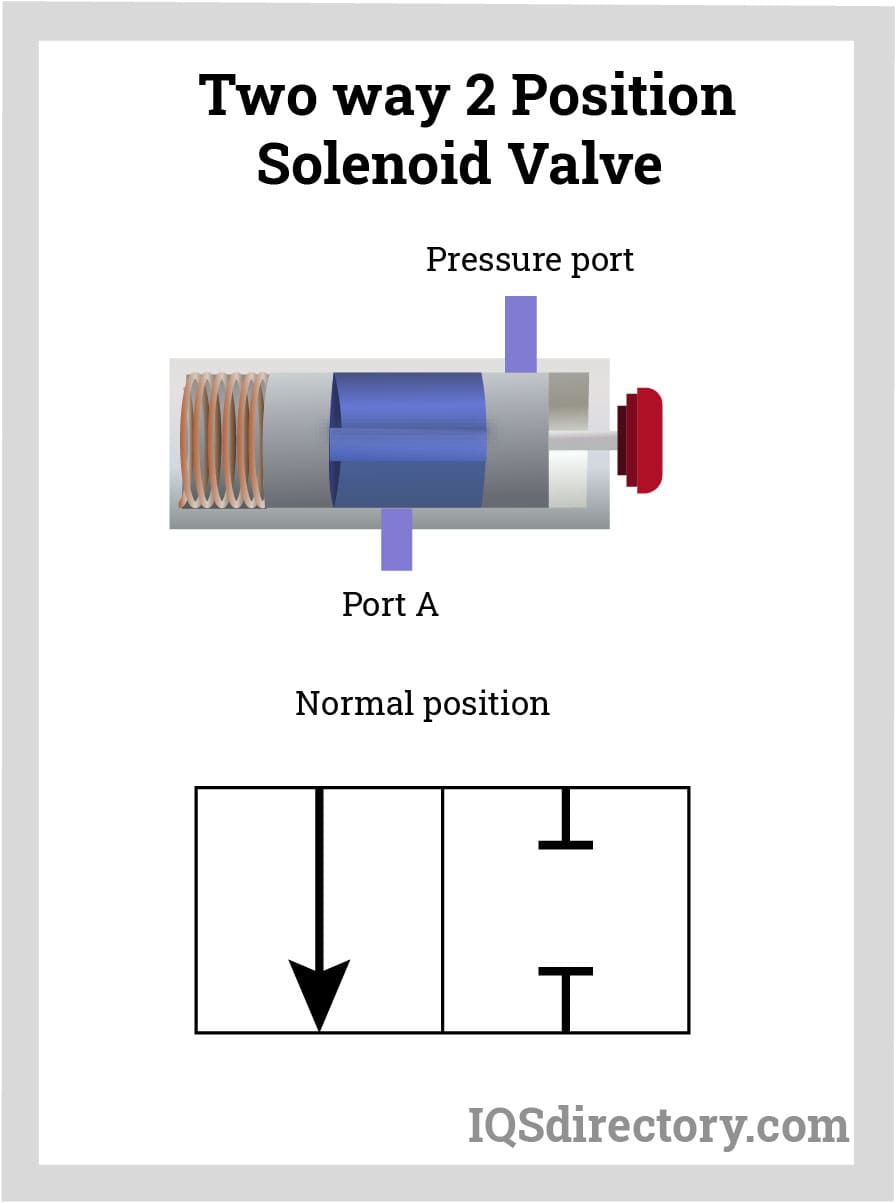
Two-way, Two-position Valves
This is a valve that has two ports linked by a channel that can be opened and closed to control the flow. In most cases, an electrically operated solenoid changes the valve's spool or poppet to guide the flow. In addition, many systems employ the valve's simple on-off function to connect, interlock and isolate different system components.
Three-way, Two-position Valves
These valves consist of three ports joined by internal valve body channels. To control a single-acting cylinder, the valves either pilot another valve or pressurize and exhaust one output port. Pressurized air is sent to the cylinder's cap-end side by three-way valves. The actuator is shielded from flow and pressure when the spool is at the opposite extreme. Given that the actuator is attached to the exhaust tube, the rod must return to its initial position due to gravity or spring force.
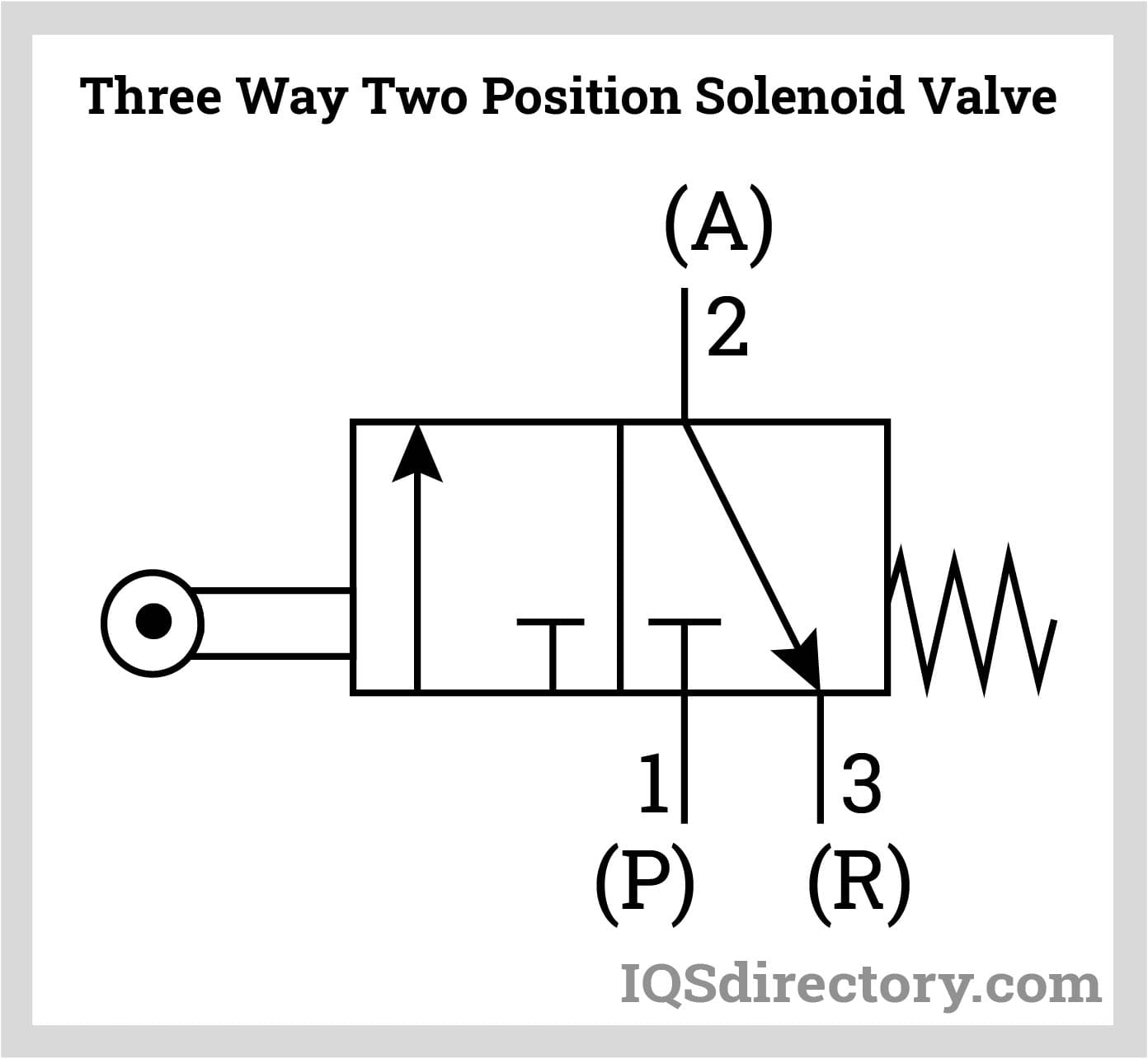
A pair of three-way valves can operate a double-acting cylinder instead of a four-way valve. Consider using paired three-way valves instead of four-way valves when high cylinder speeds are necessary—tightly fastening three-way valves to the cylinder ports decreases cylinder backpressure and pressure loss in the lines, allowing for higher cylinder velocities. Additionally, the valves are employed in high-cyclic applications or when intermediate positions are necessary to conserve compressed air.
Pneumatic Valve Specifications
Pneumatic valves are subject to several standards, some of which are reviewed here. However, every supplier and valve manufacturer may describe their valves differently; this article is intended to provide broad guidance. Additionally, the precise specifications depend on several factors, including the intended porting, the manifold design, and the valve actuation mechanism.
- The operating pressure, or pressure range, refers to the range of pressures that the valve is intended to endure ( in psi, Bars, or Pa).
- The different types of fluid that the valve can safely control serve as its operating medium. In most equipment, this is compressed air.
- A measure of a valve's ability to pass or flow air through it, flow capacity or flow coefficient (Cv) expresses the proportionality constant between flow rate and differential pressure.
- The time needed for an actuated valve to change states or positions is known as the response time.
- The greatest number of valve cycles a valve may complete in a specific period is known as the cycle rate.
- Coil-rated voltage, measured in both DC and AC volts, is the maximum voltage an electrically operated valve's actuation coil can produce.
- Port size: The actual dimensional features of the equipment define the port sizes and thread types.
Choosing the Proper Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Manufacturer
To make sure you have the most beneficial outcome when purchasing pneumatic solenoid valves from a pneumatic solenoid valve manufacturer, it is important to compare at least 4 to 5 companies using our list of pneumatic solenoid valve manufacturers. Each pneumatic solenoid valve manufacturer has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each pneumatic solenoid valve company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple pneumatic solenoid valve companies with the same quote.



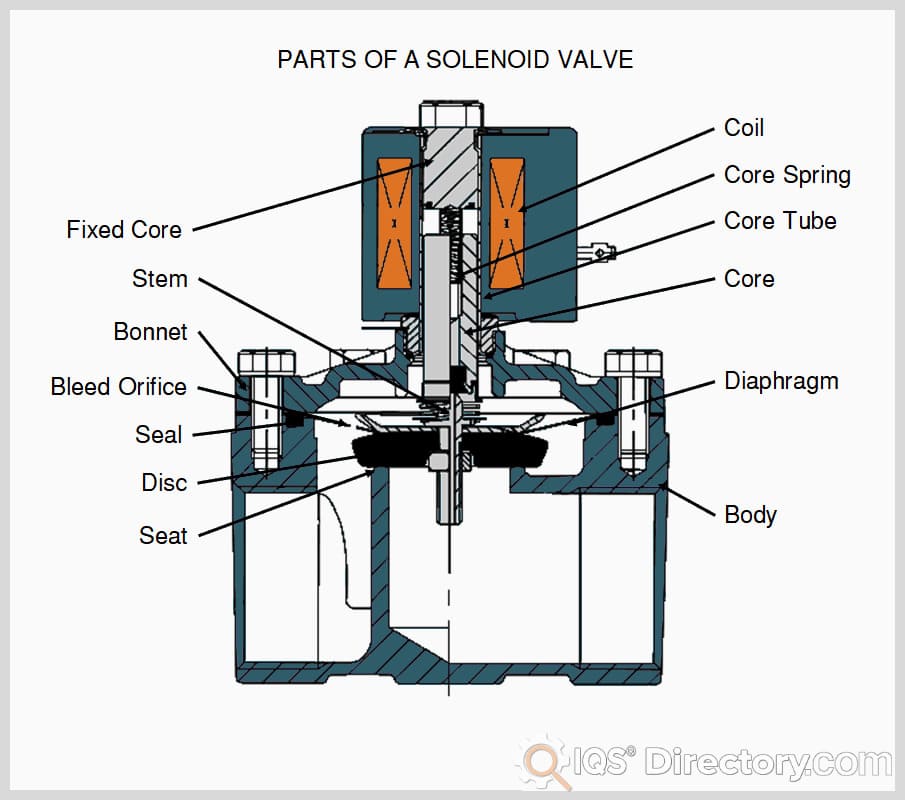

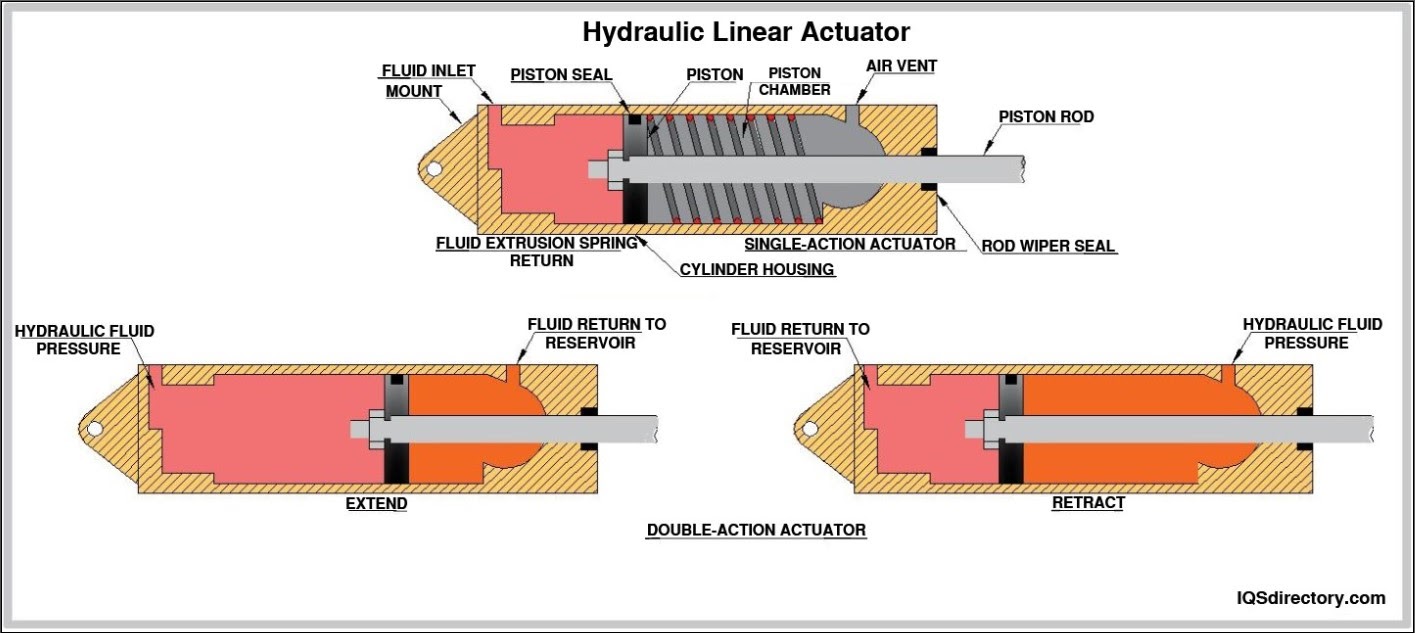
 Ball Valves
Ball Valves Butterfly Valves
Butterfly Valves Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps Check Valves
Check Valves Diaphragm Valves
Diaphragm Valves Flow Meters
Flow Meters Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic Pumps Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic Valves Metering Pumps
Metering Pumps Solenoid Valves
Solenoid Valves Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum Pumps Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services